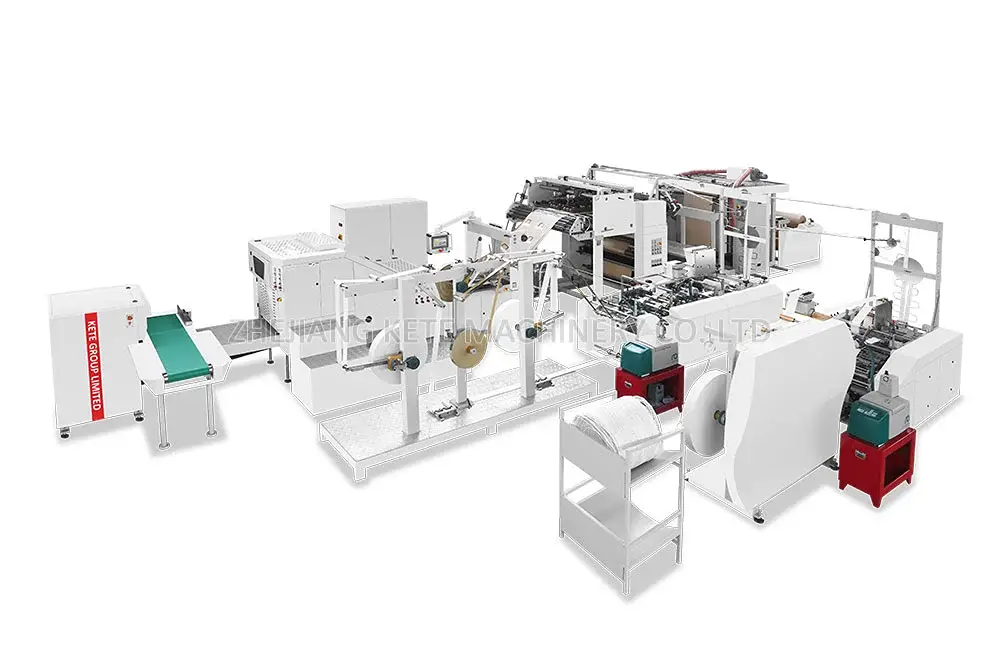
Introduction to Plastic Bag
The use of plastic bags has become an integral part of our daily lives. From zipping to the grocery store to wrapping up our sandwiches, these different types of plastic bags are the real deal! We’ve got the zippy ones, the big trashy ones, and even the earth-hugging biodegradable plastic bags. Ever wondered how is a plastic bag made? The journey from tiny plastic pellets to a finished bag is a fascinating industrial process, centered around a technology known as Blown Film Extrusion. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly how to make plastic bags.
7 Steps: How to Make Plastic Bags?
Ever wondered how a simple plastic bag comes to life? The plastic bag manufacturing process involves a series of intricate steps, each contributing to the bag’s final form. Let’s have a closer look at the plastic production process.
| Step | Description |
| Raw Material Transformation | Raw polymers (derived from natural gas or petroleum) are transformed into plastic resin pellets through heating and pressure in machines like pelletizers. |
| Extrusion Process | The resin pellets are fed into an extruder, melted, and forced through a circular die to form a continuous plastic film tube. |
| Blown Film | The film tube is inflated with air, like a balloon, to stretch it to the desired thickness. |
| Cooling and Setting | The plastic film is rapidly cooled using air or water cooling systems to solidify it and ensure uniform thickness. |
| Coloring and Additive Mixing | Dyes and additives (e.g., UV stabilizers, tear resistance agents) are mixed into the molten plastic to give the film color and enhance its properties. |
| Cutting and Sealing | The plastic film is cut into specific lengths, and the bottom is heat-sealed to form the bag’s base. |
| Printing (Optional) | Flexographic printing is used to apply logos, text, or designs onto the bags. |
| Quality Control and Testing | The bags undergo rigorous tests for thickness, strength, UV resistance, and other properties to ensure they meet quality standards. |
| Packaging and Distribution | The finished plastic bags are counted, stacked, packaged, and prepared for shipping to retailers or consumers. |
From Polymers to Resin Pellets: The Transformation
Polymers are the raw materials, often coming from natural gas or crude oil, that are the starting point for your plastic bag. Before they become the bags that carry your groceries or your lunch, they must first undergo a significant transformation. These polymers are turned into what we call plastic resin pellets. Think of these plastic pellets as the fundamental building blocks; they are the basic units that will be used to create a durable and functional plastic bag..
Now, how does this metamorphosis happen? The process involves a series of controlled stages. First, the raw polymers are subjected to carefully controlled heat and pressure in specialized machines like pelletizers. The quality of these initial pellets directly impacts the final product, which is why the entire manufacturing line, from the extruder onwards, must be robust. This breaks down their complicated chains into simpler, more manageable forms. This process yields small, cylindrical pellets. These pellets are the go-to material for the next steps because they’re consistent and easy to work with.
These aren’t just any old pellets. They are precisely formulated with additives like colorants or UV stabilizers. So, when you see a plastic bag that’s a particular color or extra tough, it’s all thanks to the special recipe of these resin pellets.
In short, this initial stage of turning polymers into resin pellets is critical for the steps that follow. It sets the mood and prepares the stage for the main event. You can’t just skip it and expect a great show.
The Extrusion Process: Crafting the Plastic Film from Extruder
The film extrusion process is where the crucial transformation begins. The resin pellets are loaded into an extruder, a machine that’s about to give our plastic bag its shape.
This is the heart of the manufacturing line. In the industry, this entire stage is called the Blown Film Extrusion process. The molten plastic is forced through a circular die, which shapes it into a continuous tube of thin plastic film. As the tube exits the die, it is pulled upwards and inflated with air, like a long balloon. This stretching is what creates the thin, strong film.
As the plastic exits the extruder, it’s cooled down rapidly using cold air or water. This sudden cooling solidifies the plastic, turning it into a film. The thickness of this film can be adjusted based on the desired properties of the final bag. Need a heavy-duty bag for carrying bricks? You’ll want a thicker film. Looking for a lightweight bag for carrying a sandwich? A thinner film will do the trick.
But here’s a fun fact: the plastic film isn’t flat when it comes out of the extruder. It’s actually tubular. If you’ve ever noticed that most plastic shopping bags are seamless on the sides, this is why. They’re cut from a continuous tube of plastic, ensuring strength and durability.
The extrusion process is a testament to the marvels of modern manufacturing. It’s a blend of science, engineering, and a touch of artistry, ensuring that the plastic film is just right for its intended purpose.
Coloring and Adding Additives
Once we have our plastic film, it’s time to give it some personality. While the natural color of polyethylene is somewhat translucent, plastic bags come in a myriad of colors, from opaque to transparent. How’s that done? Enter the world of dyes and additives.
Dyes are mixed with the molten plastic before it’s extruded, ensuring an even color throughout the film. Whether you want a vibrant red or a subtle blue, it’s all about getting the right mix of dyes.
But color isn’t the only thing added to our bags. Additives play a crucial role in enhancing the final plastic bag properties. Need a bag that can withstand sunlight without degrading? UV stabilizers are added. Want a bag that’s more flexible or resistant to tears? There are additives for that too. This allows the bag’s final properties to be tailored for its intended use.
Cooling and Setting the Film
Once the plastic exits the extruder, it’s in a somewhat vulnerable state. It’s warm, malleable, and not yet in its final form. This is where the cooling process comes into play. Cooling isn’t just about bringing the temperature down; it’s about ensuring the plastic sets correctly, maintaining its desired thickness and strength.
Air-cooling systems blow cold air onto the film, solidifying it rapidly. In some cases, water cooling systems are used, where the film is passed over chilled rollers. This rapid cooling is crucial. If the film cools too slowly, it can become uneven or develop imperfections. Think of it like chocolate; if it doesn’t cool uniformly, it can become grainy or discolored. The efficiency of the cooling ring is a major factor in production speed. A well-designed air ring, for example, provides a uniform airflow that cools the bubble evenly, preventing weak spots and allowing the machine to run faster without sacrificing quality.
During this phase, rollers also play a pivotal role. They ensure the film is stretched uniformly, preventing any wrinkles or folds. It’s a delicate balance of temperature and tension, ensuring the film is just right.
Cutting and Sealing
With our film set and ready, it’s time to transform it into recognizable bags. But how do we go from a continuous roll of plastic film to individual bags? The answer lies in precision cutting and sealing. Before the bags are cut, the rolls of plastic film are often sent to a printing press. Here, logos, text, and graphics are printed onto the film using a process called flexography, which is fast and efficient for large-scale production.
The film is fed into machines that cut it at regular intervals, determining the bag’s length. But a bag isn’t just about length; it needs a base. This is where sealing comes into play. The bottom of each cut section is sealed using heat. This heat fuses the plastic together, creating a strong bond that forms the bag’s base. It’s essential this seal is robust; it’s what gives the bag its carrying capacity.
The top remains open, ready for use. In some cases, additional features like handles or zippers are added, further enhancing the bag’s functionality.
Quality Control: Testing for Thickness, Strength, and Other Desired Properties
Quality control is the unsung hero in the world of plastic bag production. After all, no one wants a bag that tears under the slightest pressure. So, how are plastic bags made to be consistent in quality? Through rigorous testing.
Each batch of bags undergoes a series of tests. The thickness of the bags is measured to ensure uniformity. After all, a bag that’s too thin might not hold up, while one that’s too thick could be wasteful.
Strength tests are also paramount. Bags are filled and stretched to their limits, ensuring they meet the standards set by manufacturers. Other tests might include exposure to UV light (to check resistance to sun damage) or moisture tests (to verify the bag’s ability to repel water).
Packaging for Distribution
Once the bags pass their tests with flying colors, they’re ready to be sent out into the world. But first, they need to be packaged. Machines count and stack the bags, preparing them for distribution. They’re then boxed up, ready to be shipped to retailers or directly to consumers.
Types of Polymers Used: What are Plastic Bags Made of?
Ever wondered what the plastic bags in your hand actually made of? Well, you’re not alone. The types of polymers used in these bags are more than just a mouthful to say; they’re the backbone of the plastic bag’s many uses.
Polyethylene
Let’s start with the big one: polyethylene. It’s the most common material you’ll find in plastic bags. Originating from natural gas and petroleum, polyethylene goes through a whole manufacturing process to become the bags we use daily. There are different types, like low density polyethylene (LDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), linear low-density polyethylene(LLDPE).
LDPE is what you’ll find in those softer, more flexible, and typically more transparent bags—think produce bags at the grocery store.
HDPE is sturdier, more opaque or translucent, and is what you’re holding when you’ve got a bag full of canned goods.
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) is tougher and has a higher tensile strength than LDPE. It’s often used in stretch films, toys, and some flexible containers.
Polypropylene
Then there’s polypropylene, the other heavy hitter in the plastic bag world. This one’s got a higher melting point, so it’s the go-to for anything that needs to withstand some heat. You’ll often find polypropylene in reusable shopping bags. Plus, it’s hydrophobic, meaning it’s excellent at repelling water.
A Note on Additives and Colorants
It’s important to know that these base polymers are often just the starting point. To achieve specific properties, manufacturers mix in various additives. For instance, color masterbatch (a concentrated pigment) is added to create bags of any color, UV stabilizers are included to prevent the plastic from degrading in sunlight, and anti-static agents can be used to stop bags from clinging together. These additions are what give a plastic bag its final look, feel, and specific function.
So, whether it’s polyethylene or polypropylene, and with a little help from additives, each bag has its own set of perks that make it the right fit for different jobs.
The Immense Benefits of the Plastic Bag
There’s a whole bunch of reasons we can’t live without plastic bags. But let’s just chat about the highlights and key plastic bag properties that make them an important part of our everyday life.
| Lightweight | One of the most significant advantages of plastic bags is their lightweight nature. This feature not only makes it easy to carry but also reduces transportation costs. When you’re shipping products, every ounce counts, and plastic bags offer a lightweight yet sturdy solution that can lead to substantial cost savings. |
| Durable | Appearances can be deceiving. Despite their thin structure, plastic bags are incredibly durable. Thanks to the high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) used in their manufacturing process, these bags can hold a considerable amount of weight without tearing. This durability makes them a go-to choice for grocery stores and retail outlets. |
| Withstand Moisture | Another remarkable feature of plastic bags is their ability to resist moisture. Your groceries stay dry even when it’s pouring outside. That’s the magic of plastic. Materials like polypropylene are particularly effective at keeping moisture at bay, making plastic bags ideal for food storage and other moisture-sensitive applications. |
| Versatility | Plastic bags come in all shapes and sizes, making them incredibly versatile. Whether you’re shopping for clothes, groceries, or electronics, there’s a plastic bag designed to meet your needs. The variety extends to features like handles, zipper storage bags, and even the type of seal, offering a range of options for both consumers and businesses. Additionally, bag-in-box packaging is often used for liquids such as box wine and institutional sizes of other liquids. This type of packaging provides a convenient and efficient way to store and transport liquids, reducing the need for single-use plastic bags. |
These benefits showcase the immense utility of plastic bags, making them more than just a convenience; they’re a product of thoughtful engineering and design.

Sustainability in Production: What Happens to Waste Material?
The Eco-Friendly Behind-the-Scenes When crafting plastic bags, there’s a bit of behind-the-scenes action that doesn’t make it to the final cut. We’re talking about the off-cuts, the “oops-that’s-not-right” bags, and the leftovers that didn’t quite make it out of the machines. But in today’s green-conscious world, we don’t just sweep them under the rug.
Recycling: The Green Comeback A good slice of this backstage waste is ready for an encore. Off-cuts and those bags that didn’t pass the audition can be gathered, can be gathered, melted down, and reprocessed into new bags. This recycling loop is an efficient way to reuse raw materials in plastic production, cutting down the need for fresh polymers. It’s not just eco-friendly; it’s also kind to the manufacturer’s wallet.
Disposal: The Thoughtful Exit But let’s face it, not every piece of waste is ready for a second act. Some, due to mixed materials or other issues, just can’t be recycled and reused. But even these get a dignified exit. Instead of being sent directly to a landfill, they’re often incinerated in a controlled setting, keeping the environment’s best interests at heart. And the cherry on top? Some top-notch facilities turn the energy from this process into electricity. Now that’s a bright idea!
Conclusion
From the initial melting of polymer pellets to the final cut and seal, understanding how a plastic bag is made reveals a process of precision engineering. The process of blown film extrusion, followed by automated conversion, transforms simple raw materials into a durable and versatile everyday item. Now that you’ve seen the intricate steps involved, you have a deeper appreciation for the technology and science behind this ubiquitous product.
Kickstart Your Plastic Bag Venture with KETE
Understanding how plastic bags are made is the first step. Bringing them to life requires precision machinery engineered for efficiency and quality. The blown film extruders, printing presses, and bag-making machines are all critical components of a successful production line.
If you’re considering entering the plastic bag industry or want to upgrade your current operations, having the right technology partner is key. At KETE, we don’t just supply machines; we provide complete solutions tailored to your production goals. Contact our experts for a technical consultation or to get a quote on a production line that fits your needs.
FAQS
Q: How much of plastic bags are actually recycled?
A: Although plastic bags are technically recyclable, less than 10% of them are actually recycled. Most end up in landfills, incinerators, or the environment due to contamination, mixed materials, or the lack of specialized recycling facilities.
Q: What are plastic bags actually made of?
A: Plastic bags are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), both of which are petroleum-based plastics. These materials are lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant, making them ideal for packaging and retail use.
Q: Why can’t Ziploc bags be recycled?
A: Ziploc bags are often made of recyclable polyethylene, but they’re frequently contaminated with food residue, oils, or moisture, which makes them difficult to process through standard curbside recycling programs. Additionally, their zipper seals can include mixed materials. However, some grocery stores offer drop-off bins specifically for clean, dry plastic films, including Ziploc bags.
Q: How many years does it take for plastic bags to decompose naturally?
A: Plastic bags can take 500 to 1,000 years to break down in the environment. Even then, they don’t fully biodegrade — they fragment into microplastics, which persist in ecosystems and pose long-term threats to wildlife and human health.