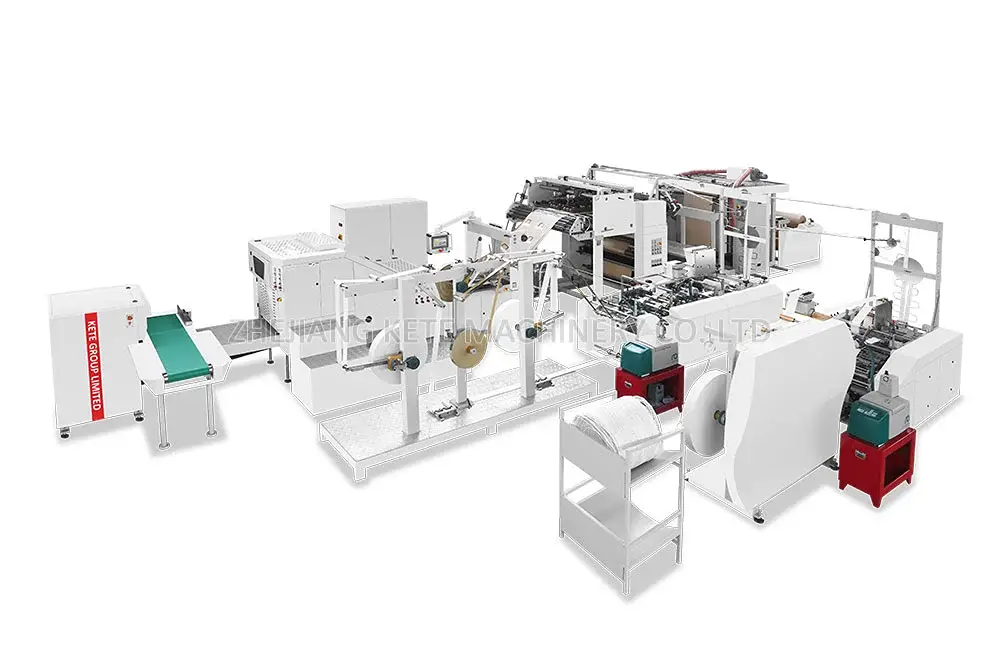
Giới thiệu về túi nhựa
The use of plastic bags has become an integral part of our daily lives. From zipping to the grocery store to wrapping up our sandwiches, these different types of plastic bags are the real deal! We’ve got the zippy ones, the big trashy ones, and even the earth-hugging biodegradable plastic bags. Ever wondered how is a plastic bag made? The journey from tiny plastic pellets to a finished bag is a fascinating industrial process, centered around a technology known as Blown Film Extrusion. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly how to make plastic bags.
7 Steps: How to Make Plastic Bags?
Bạn đã bao giờ tự hỏi một chiếc túi nhựa đơn giản trở nên như thế nào chưa? Quy trình sản xuất túi nhựa bao gồm một loạt các bước phức tạp, mỗi bước đều góp phần tạo nên hình dạng cuối cùng của chiếc túi. Hãy cùng tìm hiểu kỹ hơn về quy trình sản xuất nhựa.
| Bước chân | Sự miêu tả |
| Thô Material Transformation | Raw polymers (derived from natural gas or petroleum) are transformed into plastic resin pellets through heating and pressure in machines like pelletizers. |
| Extrusion Process | The resin pellets are fed into an extruder, melted, and forced through a circular die to form a continuous plastic film tube. |
| Blown Film | The film tube is inflated with air, like a balloon, to stretch it to the desired thickness. |
| Cooling and Setting | The plastic film is rapidly cooled using air or water cooling systems to solidify it and ensure uniform thickness. |
| Coloring and Additive Mixing | Dyes and additives (e.g., UV stabilizers, tear resistance agents) are mixed into the molten plastic to give the film color and enhance its properties. |
| Cắt và niêm phong | The plastic film is cut into specific lengths, and the bottom is heat-sealed to form the bag’s base. |
| Printing (Optional) | Flexographic printing is used to apply logos, text, or designs onto the bags. |
| Quality Control and Testing | The bags undergo rigorous tests for thickness, strength, UV resistance, and other properties to ensure they meet quality standards. |
| Đóng gói và phân phối | The finished plastic bags are counted, stacked, packaged, and prepared for shipping to retailers or consumers. |
Từ Polymer đến Viên Nhựa: Sự Chuyển Đổi
Polymers are the raw materials, often coming from natural gas or crude oil, that are the starting point for your plastic bag. Before they become the bags that carry your groceries or your lunch, they must first undergo a significant transformation. These polymers are turned into what we call plastic resin pellets. Think of these plastic pellets as the fundamental building blocks; they are the basic units that will be used to create a durable and functional plastic bag..
Now, how does this metamorphosis happen? The process involves a series of controlled stages. First, the raw polymers are subjected to carefully controlled heat and pressure in specialized machines like pelletizers. The quality of these initial pellets directly impacts the final product, which is why the entire manufacturing line, from the extruder onwards, must be robust. This breaks down their complicated chains into simpler, more manageable forms. This process yields small, cylindrical pellets. These pellets are the go-to material for the next steps because they’re consistent and easy to work with.
These aren’t just any old pellets. They are precisely formulated with additives like colorants or UV stabilizers. So, when you see a plastic bag that’s a particular color or extra tough, it’s all thanks to the special recipe of these resin pellets.
In short, this initial stage of turning polymers into resin pellets is critical for the steps that follow. It sets the mood and prepares the stage for the main event. You can’t just skip it and expect a great show.
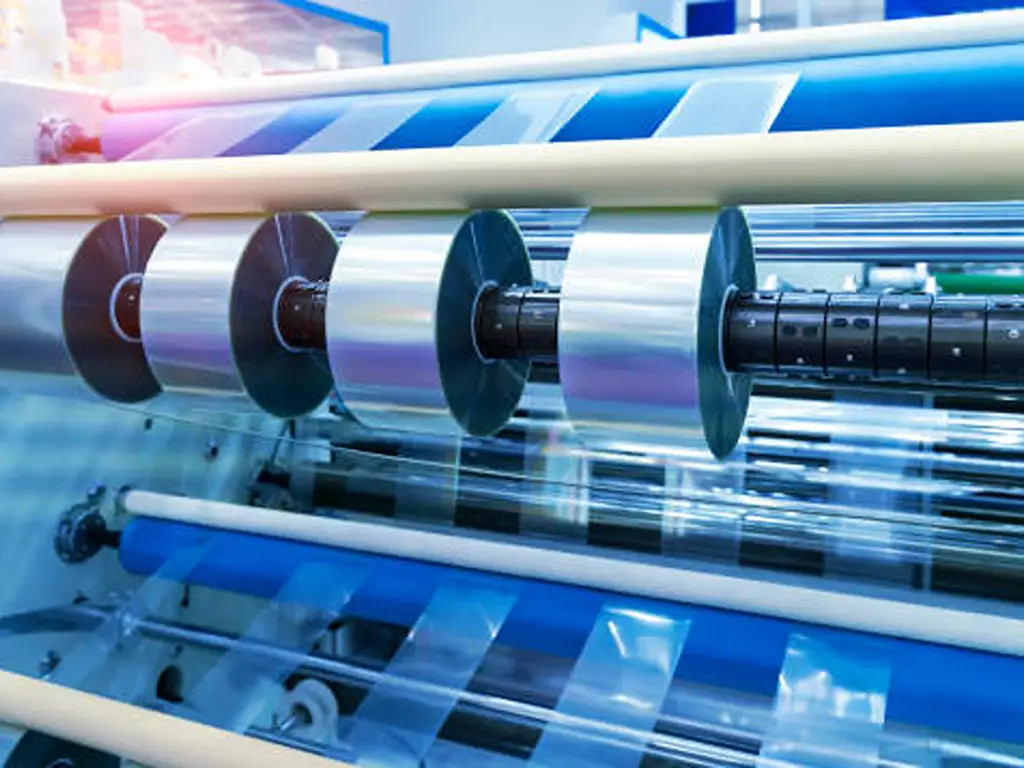
The Extrusion Process: Crafting the Plastic Film from Extruder
The film extrusion process is where the crucial transformation begins. The resin pellets are loaded into an extruder, a machine that’s about to give our plastic bag its shape.
This is the heart of the manufacturing line. In the industry, this entire stage is called the Blown Film Extrusion process. The molten plastic is forced through a circular die, which shapes it into a continuous tube of thin plastic film. As the tube exits the die, it is pulled upwards and inflated with air, like a long balloon. This stretching is what creates the thin, strong film.
Khi nhựa thoát khỏi máy đùn, nó được làm mát nhanh chóng bằng không khí lạnh hoặc nước. Quá trình làm mát đột ngột này làm đông cứng nhựa, biến nó thành một lớp màng. Độ dày của lớp màng này có thể được điều chỉnh dựa trên các đặc tính mong muốn của túi cuối cùng. Cần một chiếc túi chịu lực để đựng gạch? Bạn sẽ muốn một lớp màng dày hơn. Đang tìm một chiếc túi nhẹ để đựng bánh sandwich? Một lớp màng mỏng hơn sẽ là giải pháp.
Nhưng đây là một sự thật thú vị: màng nhựa không phẳng khi ra khỏi máy đùn. Thực ra nó có dạng ống. Nếu bạn từng nhận thấy rằng hầu hết các túi mua sắm bằng nhựa đều không có đường may ở hai bên, thì đây là lý do. Chúng được cắt từ một ống nhựa liên tục, đảm bảo độ bền và chắc chắn.
Quá trình đùn là minh chứng cho sự kỳ diệu của sản xuất hiện đại. Đó là sự kết hợp giữa khoa học, kỹ thuật và một chút nghệ thuật, đảm bảo rằng màng nhựa hoàn toàn phù hợp với mục đích sử dụng.
Tô màu và thêm phụ gia
Khi đã có màng nhựa, đã đến lúc thêm chút cá tính cho nó. Trong khi màu tự nhiên của polyethylene là hơi trong mờ, túi nhựa có vô số màu sắc, từ đục đến trong suốt. Làm thế nào để thực hiện điều đó? Hãy bước vào thế giới thuốc nhuộm và chất phụ gia.
Thuốc nhuộm được trộn với nhựa nóng chảy trước khi đùn, đảm bảo màu sắc đồng đều trên toàn bộ màng phim. Cho dù bạn muốn màu đỏ rực rỡ hay màu xanh lam tinh tế, tất cả đều phụ thuộc vào việc pha trộn thuốc nhuộm phù hợp.
But color isn’t the only thing added to our bags. Additives play a crucial role in enhancing the final plastic bag properties. Need a bag that can withstand sunlight without degrading? UV stabilizers are added. Want a bag that’s more flexible or resistant to tears? There are additives for that too. This allows the bag’s final properties to be tailored for its intended use.
Làm mát và thiết lập phim
Khi nhựa ra khỏi máy đùn, nó ở trạng thái khá dễ bị tổn thương. Nó ấm, dễ uốn và chưa ở dạng cuối cùng. Đây là lúc quá trình làm mát phát huy tác dụng. Làm mát không chỉ là hạ nhiệt độ xuống; mà còn là đảm bảo nhựa đông lại đúng cách, duy trì độ dày và độ bền mong muốn.
Air-cooling systems blow cold air onto the film, solidifying it rapidly. In some cases, water cooling systems are used, where the film is passed over chilled rollers. This rapid cooling is crucial. If the film cools too slowly, it can become uneven or develop imperfections. Think of it like chocolate; if it doesn’t cool uniformly, it can become grainy or discolored. The efficiency of the cooling ring is a major factor in production speed. A well-designed air ring, for example, provides a uniform airflow that cools the bubble evenly, preventing weak spots and allowing the machine to run faster without sacrificing quality.
Trong giai đoạn này, con lăn cũng đóng vai trò then chốt. Chúng đảm bảo màng phim được kéo căng đồng đều, ngăn ngừa bất kỳ nếp nhăn hoặc nếp gấp nào. Đó là sự cân bằng tinh tế giữa nhiệt độ và độ căng, đảm bảo màng phim ở mức vừa phải.
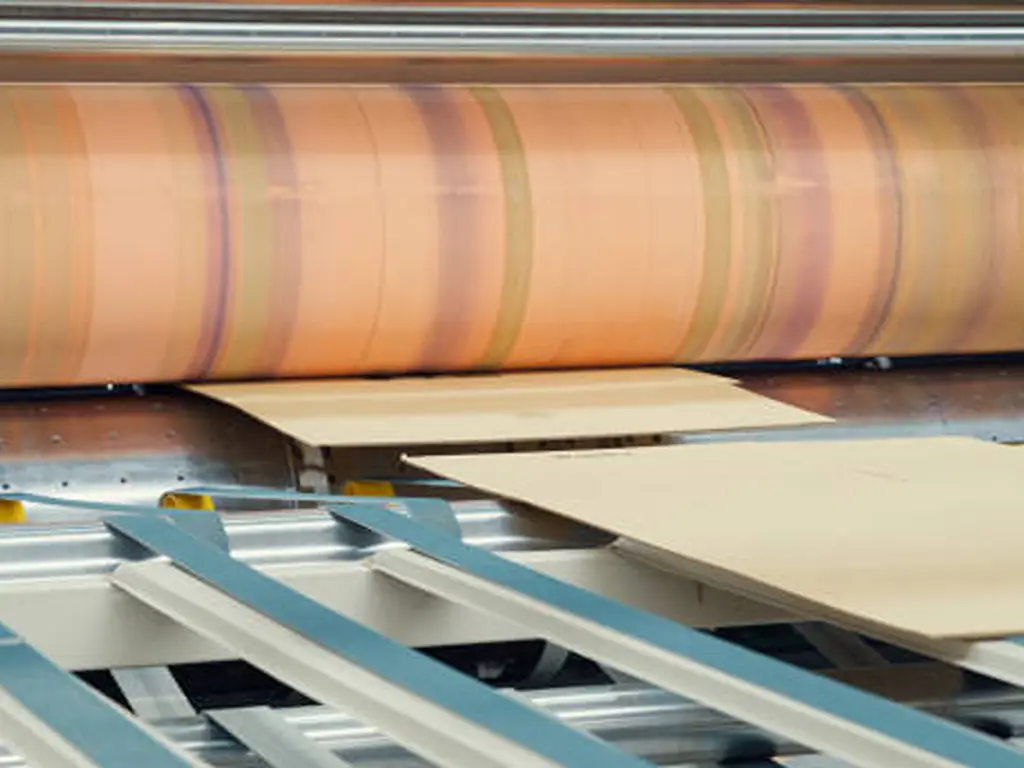
Cắt và niêm phong
With our film set and ready, it’s time to transform it into recognizable bags. But how do we go from a continuous roll of plastic film to individual bags? The answer lies in precision cutting and sealing. Before the bags are cut, the rolls of plastic film are often sent to a printing press. Here, logos, text, and graphics are printed onto the film using a process called flexography, which is fast and efficient for large-scale production.
Màng phim được đưa vào máy cắt theo các khoảng thời gian đều đặn, xác định chiều dài của túi. Nhưng một chiếc túi không chỉ có chiều dài; nó cần một đế. Đây là nơi mà việc niêm phong phát huy tác dụng. Đáy của mỗi phần cắt được niêm phong bằng nhiệt. Nhiệt này làm cho nhựa kết dính lại với nhau, tạo ra một liên kết chắc chắn tạo thành đế của túi. Điều cần thiết là lớp niêm phong này phải chắc chắn; đó là thứ tạo nên sức chứa của túi.
Phần trên vẫn mở, sẵn sàng sử dụng. Trong một số trường hợp, các tính năng bổ sung như tay cầm hoặc khóa kéo được thêm vào, giúp tăng cường thêm chức năng của túi.
Kiểm soát chất lượng: Kiểm tra độ dày, độ bền và các đặc tính mong muốn khác
Kiểm soát chất lượng là người hùng thầm lặng trong thế giới sản xuất túi nhựa. Rốt cuộc, không ai muốn một chiếc túi bị rách dưới áp lực nhỏ nhất. Vậy, túi nhựa được sản xuất như thế nào để có chất lượng đồng đều? Thông qua thử nghiệm nghiêm ngặt.
Mỗi lô túi đều trải qua một loạt các thử nghiệm. Độ dày của túi được đo để đảm bảo tính đồng nhất. Rốt cuộc, một chiếc túi quá mỏng có thể không giữ được, trong khi một chiếc túi quá dày có thể gây lãng phí.
Các thử nghiệm về độ bền cũng rất quan trọng. Túi được nhồi và kéo căng đến giới hạn, đảm bảo chúng đáp ứng các tiêu chuẩn do nhà sản xuất đặt ra. Các thử nghiệm khác có thể bao gồm tiếp xúc với tia UV (để kiểm tra khả năng chống lại tác hại của ánh nắng mặt trời) hoặc thử độ ẩm (để xác minh khả năng chống nước của túi).
Bao bì để phân phối
Khi những chiếc túi vượt qua các bài kiểm tra với kết quả tốt, chúng đã sẵn sàng để được gửi ra thế giới. Nhưng trước tiên, chúng cần được đóng gói. Máy móc sẽ đếm và xếp chồng các túi, chuẩn bị cho việc phân phối. Sau đó, chúng được đóng hộp, sẵn sàng để vận chuyển đến các nhà bán lẻ hoặc trực tiếp đến người tiêu dùng.
Các loại polyme được sử dụng: Túi nhựa được làm từ gì?
Bạn có bao giờ tự hỏi những chiếc túi nhựa trong tay bạn thực sự được làm từ gì không? Vâng, bạn không phải là người duy nhất. Các loại polyme được sử dụng trong những chiếc túi này không chỉ là một cái tên để gọi; chúng là xương sống của nhiều công dụng của túi nhựa.
Polyetylen
Let’s start with the big one: polyethylene. It’s the most common material you’ll find in plastic bags. Originating from natural gas and petroleum, polyethylene goes through a whole manufacturing process to become the bags we use daily. There are different types, like low density polyethylene (LDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), linear low-density polyethylene(LLDPE).
LDPE is what you’ll find in those softer, more flexible, and typically more transparent bags—think produce bags at the grocery store.
HDPE is sturdier, more opaque or translucent, and is what you’re holding when you’ve got a bag full of canned goods.
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) is tougher and has a higher tensile strength than LDPE. It’s often used in stretch films, toys, and some flexible containers.
Polypropylen
Sau đó là polypropylene, một loại vật liệu nặng ký khác trong thế giới túi nhựa. Loại này có điểm nóng chảy cao hơn, vì vậy nó là lựa chọn cho bất kỳ thứ gì cần chịu được nhiệt. Bạn thường thấy polypropylene trong túi mua sắm có thể tái sử dụng. Thêm vào đó, nó kỵ nước, nghĩa là nó rất tuyệt vời trong việc đẩy nước.
A Note on Additives and Colorants
It’s important to know that these base polymers are often just the starting point. To achieve specific properties, manufacturers mix in various additives. For instance, color masterbatch (a concentrated pigment) is added to create bags of any color, UV stabilizers are included to prevent the plastic from degrading in sunlight, and anti-static agents can be used to stop bags from clinging together. These additions are what give a plastic bag its final look, feel, and specific function.
So, whether it’s polyethylene or polypropylene, and with a little help from additives, each bag has its own set of perks that make it the right fit for different jobs.
Lợi ích to lớn của túi nhựa
There’s a whole bunch of reasons we can’t live without plastic bags. But let’s just chat about the highlights and key plastic bag properties that make them an important part of our everyday life.
| Nhẹ | Một trong những lợi thế quan trọng nhất của túi nhựa là tính chất nhẹ của chúng. Tính năng này không chỉ giúp dễ dàng mang theo mà còn giảm chi phí vận chuyển. Khi bạn vận chuyển sản phẩm, mỗi ounce đều có giá trị và túi nhựa cung cấp giải pháp nhẹ nhưng chắc chắn có thể giúp tiết kiệm chi phí đáng kể. |
| Bền bỉ | Vẻ bề ngoài có thể đánh lừa. Mặc dù có cấu trúc mỏng, nhưng túi nhựa lại cực kỳ bền. Nhờ polyethylene mật độ cao (HDPE) và polyethylene mật độ thấp (LDPE) được sử dụng trong quy trình sản xuất, những chiếc túi này có thể chứa được một lượng lớn trọng lượng mà không bị rách. Độ bền này khiến chúng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu cho các cửa hàng tạp hóa và cửa hàng bán lẻ. |
| Chịu được độ ẩm | Một đặc điểm đáng chú ý khác của túi nhựa là khả năng chống ẩm. Hàng tạp hóa của bạn vẫn khô ráo ngay cả khi trời đổ mưa bên ngoài. Đó chính là điều kỳ diệu của nhựa. Các vật liệu như polypropylene đặc biệt hiệu quả trong việc giữ ẩm, khiến túi nhựa trở nên lý tưởng để bảo quản thực phẩm và các ứng dụng nhạy cảm với độ ẩm khác. |
| Tính linh hoạt | Túi nhựa có đủ mọi hình dạng và kích cỡ, khiến chúng trở nên vô cùng linh hoạt. Cho dù bạn đang mua sắm quần áo, hàng tạp hóa hay đồ điện tử, đều có một loại túi nhựa được thiết kế để đáp ứng nhu cầu của bạn. Sự đa dạng này mở rộng đến các tính năng như quai xách, túi đựng có khóa kéo và thậm chí cả loại niêm phong, mang đến nhiều lựa chọn cho cả người tiêu dùng và doanh nghiệp. Ngoài ra, bao bì dạng túi trong hộp thường được sử dụng cho các chất lỏng như rượu vang hộp và các kích cỡ theo tiêu chuẩn của tổ chức đối với các chất lỏng khác. Loại bao bì này cung cấp một cách thuận tiện và hiệu quả để lưu trữ và vận chuyển chất lỏng, giúp giảm nhu cầu sử dụng túi nhựa dùng một lần. |
Những lợi ích này cho thấy tiện ích to lớn của túi nhựa, khiến chúng không chỉ là sự tiện lợi; mà còn là sản phẩm của quá trình thiết kế và kỹ thuật chu đáo.

Sustainability in Production: What Happens to Waste Material?
Hậu trường thân thiện với môi trường Khi làm túi nhựa, có một chút hành động hậu trường không được đưa vào bản cắt cuối cùng. Chúng ta đang nói về những phần thừa, những chiếc túi "ôi-ôi-không-đúng-rồi" và những thứ còn sót lại không được đưa ra khỏi máy. Nhưng trong thế giới có ý thức xanh ngày nay, chúng ta không chỉ quét chúng dưới tấm thảm.
Recycling: The Green Comeback A good slice of this backstage waste is ready for an encore. Off-cuts and those bags that didn’t pass the audition can be gathered, can be gathered, melted down, and reprocessed into new bags. This recycling loop is an efficient way to reuse raw materials in plastic production, cutting down the need for fresh polymers. It’s not just eco-friendly; it’s also kind to the manufacturer’s wallet.
Disposal: The Thoughtful Exit But let’s face it, not every piece of waste is ready for a second act. Some, due to mixed materials or other issues, just can’t be recycled and reused. But even these get a dignified exit. Instead of being sent directly to a landfill, they’re often incinerated in a controlled setting, keeping the environment’s best interests at heart. And the cherry on top? Some top-notch facilities turn the energy from this process into electricity. Now that’s a bright idea!
Phần kết luận
From the initial melting of polymer pellets to the final cut and seal, understanding how a plastic bag is made reveals a process of precision engineering. The process of blown film extrusion, followed by automated conversion, transforms simple raw materials into a durable and versatile everyday item. Now that you’ve seen the intricate steps involved, you have a deeper appreciation for the technology and science behind this ubiquitous product.
Khởi động dự án túi nhựa của bạn với KETE
Understanding how plastic bags are made is the first step. Bringing them to life requires precision machinery engineered for efficiency and quality. The blown film extruders, printing presses, and bag-making machines are all critical components of a successful production line.
If you’re considering entering the plastic bag industry or want to upgrade your current operations, having the right technology partner is key. At KETE, we don’t just supply machines; we provide complete solutions tailored to your production goals. Contact our experts for a technical consultation or to get a quote on a production line that fits your needs.
FAQS
Q: How much of plastic bags are actually recycled?
MỘT: Although plastic bags are technically recyclable, less than 10% of them are actually recycled. Most end up in landfills, incinerators, or the environment due to contamination, mixed materials, or the lack of specialized recycling facilities.
Q: What are plastic bags actually made of?
MỘT: Plastic bags are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), both of which are petroleum-based plastics. These materials are lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant, making them ideal for packaging and retail use.
Q: Why can’t Ziploc bags be recycled?
MỘT: Ziploc bags are often made of recyclable polyethylene, but they’re frequently contaminated with food residue, oils, or moisture, which makes them difficult to process through standard curbside recycling programs. Additionally, their zipper seals can include mixed materials. However, some grocery stores offer drop-off bins specifically for clean, dry plastic films, including Ziploc bags.
Q: How many years does it take for plastic bags to decompose naturally?
MỘT: Plastic bags can take 500 to 1,000 years to break down in the environment. Even then, they don’t fully biodegrade — they fragment into microplastics, which persist in ecosystems and pose long-term threats to wildlife and human health.